ERP-Integrations: the Ultimate Guide

Today, it is impossible to imagine a company without an ERP system. Given the ever increasing amount of data from the countless systems, it is difficult to maintain an overview of the company’s situation. Employees have to spend a lot of time on data reconciliation.
The solution: an integration of the ERP system with other systems through standardized interfaces. In the following article, we explain how this works and what challenges it entails.
Content
- How do ERP integrations work?
- The importance of ERP integration for companies
- Benefits of ERP integration
- ERP integration options
- Challenges of integrating ERP systems and their solutions
- Conclusion: an investment that pays off in the long term
- Which iPaaS solution suits the company
- Conclusion and summary
1.How do ERP integrations work?
1.1 Definition of ERP
ERP, short for Enterprise Resource Planning, is a tool that helps companies manage, organize, and integrate all of a company’s resources and processes into a single system.
The cloud-based systems can leverage artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning to provide intelligent automation, increased efficiency and instant insights across the enterprise. For example, internal processes can also be linked to external partners.
In a nutshell:
An ERP system offers companies the flexibility and speed to increase their efficiency and profitability in the long term and thus remain competitive.
1.2 ERP integration
ERP systems must be able to connect to a wide variety of applications and data sources. These third-party systems can be CRMs (Customer Relationship Management), social networks, HCMs (Human Capital Management) and other ERPs.
The systems are linked with the help of interfaces, the so-called APIs (Application Programming Interfaces) and customer-specific connectors. As a result, the data is transformed by an adapter in such a way that it can be interpreted by the respective systems. Programming is therefore no longer necessary. Providers of automation software usually take on the complete integration.
The respective providers can react flexibly to customer requirements and integrate individual systems.

With the help of dashboards, the company gets an overview of all information: a guarantee to increase customer satisfaction in the long term and to optimize business processes. It can also improve collaboration between departments and external partners.
Further methods of ERP integration are iPaaS (integration Platform as a Service) and ESB (Enterprise Service Bus). Above all, iPaaS is the more interesting model. Learn more about iPaaS here. ESB systems are mostly of an older generation and negligible here.
Integrations: Too many apps that are not talking to each other?
Locoia integrates your apps & systems in one
unified data warehouse
2. The importance of ERP integration for companies
ERP integration has become a key component of any IT strategy for most companies. New or updated IT solutions can be integrated into the existing infrastructure and a wide variety of applications can be connected to one another.
An integrated ERP thus offers automation and intelligence that have become indispensable in the day-to-day business.
By consolidating all data in one system, a “single point of truth” is created. A single database as the basis for decisions and control of operations.
Which departments can benefit from an integrated ERP system?
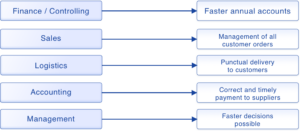
3. Benefits of ERP integration
3.1 Increase in productivity and efficiency
The intelligent automation of business processes leaves more time to concentrate on the core business and to promote the growth of the company in a resource-efficient manner.
3.2 Central data management and elimination of data silos
The systems, which are integrated via ERP software, converge on a central database and are constantly updated with data from the ongoing processes in real time.
Thus, data silos are eliminated and all departments can access the bundled data in the dashboard via a central interface. This saves a lot of time and money, because data no longer needs to be consolidated and entered manually.
3.3 Faster reporting
Annual and financial reports can be generated almost with one click. This allows business activities to be instantly adjusted to results and improve the company’s performance in real time.
3.4 Greater customer satisfaction
Bundled access to customer information and the resulting faster response times can lead to on-time deliveries. This in turn has a positive effect on customer satisfaction, which will lead to more sales in the long term.
3.5 Time and thus cost savings
The automatic consolidation of data saves employees an extremely large amount of time and labor costs compared to manually entering data into different systems.
All of the integrated data is made available to employees via a central dashboard. The time thus gained can be used for much more important things, for example in marketing and day-to-day business.
3.6 Data security and data protection
By using centralized software, it is easier to detect and defend against security threats.
Likewise, conformity with GDPR, or changes to it, is much easier to implement, as everything now only runs via one platform.
4. ERP integration options
Similar to the iPaaS integration scenarios, there are three options to integrate the software:
- Cloud (private or public)
- Cloud to on-premise
- On premise to on premise
In the following overview we explain the advantages of the first two options. The on-premise option is intentionally left out here, as it hardly ever occurs.
Cloud to cloud integration
As the name suggests, cloud to cloud integration hosts the software directly in the cloud. The main advantages are the lower initial costs and the much greater scalability. But flexibility and easier integration should not be neglected either.
The required regular updates and maintenance, as well as the responsibility for security, are taken over by the software provider.
Accordingly, as a customer, you do not need knowledge about server administration or hardware failures.
On-premise to cloud integration
The hybrid model connects the on-premise system to a public or private cloud service provider. Often this integration is used for backup and disaster recovery purposes. Last but not least, it is also used for data synchronization.
Hybrid integrations are often chosen by small and medium-sized companies, as it allows files to be stored securely in the cloud and accessed from any device.
Files can thus be stored in the cloud without having to install additional software. Users can easily share their work with each other.
5. Challenges of the integration of ERP systems and their solutions
5.1 Time-consuming implementation
The introduction of an ERP system can sometimes mean some effort in the short term, especially when it comes to the introduction of a new system. The many tasks can be daunting at first, especially customization and appropriate training for the teams. However, this is often the ideal opportunity to question one’s own business processes and, if necessary, optimize them.
Solution: agile project management
An agile approach to the project and the division into small work steps helps to keep the overview. Here “steady wins the race” applies. The more profound and well-considered decisions are made, the more sustainable the solution will be for the processes.
Many software providers also offer ERP consulting. The relevant consultants go through the processes with the customer and coordinate them.
5.2 Lack of professional knowledge of employees
In order to be able to use ERP software to its full extent, an understanding of the system and the interfaces is required. In many companies, especially small and medium-sized ones, this expertise is missing.
Solution: training courses and tutorials
A sufficient training for teams and specialist departments is recommended here. These can also be provided by the software vendor. Video tutorials are often also an option to give a detailed introduction to the application.
6. Conclusion – an investment that is worthwhile in the long term
It is well known that the integration of ERP systems can take some effort. Nevertheless, the advantages outweigh the disadvantages and help to achieve company goals: Less human error, increases in productivity and higher sales are just a few. In order to meet company-specific requirements and to achieve long-term goals, the integration of ERP with third-party systems is now an indispensable part of a promising business model.
